Croatia – key data
Area: 56,594 km² (of which land: 55,974 km², water: 620 km²)
Population: 4.5 million (2011 estimate, CIA). Composition: Croats 89.6%, Serbs 4.5%, Others 5.9% (Bosniaks,Hungary, Slovenes, Czechs and Roma) (2001 census)
Population density: 79 people per km²
Population growth: -0.076% per year (2011, CIA)
Capital: Zagreb (1.1 million residents, 2001)
Highest point: Dinara, 1,830 m
Lowest point: Adriatic Sea, 0 m
Form of government: Croatia has been a republic since 1991. The constitution dates from 1990, the last constitutional amendment was made in 2001. The Croatian unicameral parliament consists of the House of Representatives(Sabor) and consists of 152 members. Croatia has been part of the Council of Europe since 1996. The country has been independent since June 25, 1991 (secession from Yugoslavia).
Administrative division: 20 counties (zupanija, plural: zupanije): Bjelovarsko-Bilogorska, Brodsko-Posavska, Dubrovacko-Neretvanska, Istarska, Karlovacka, Koprivnicko-Krizevacka, Krapinsko-Zagorska, Licko-Senjko-Zagorska, Pozo-Senjeckka, Medimurso-ska, Osjanska, Primorsko-Goranska, Sibensko-Kninska, Sisacko-Moslavacka, Splitsko-Dalmatinska, Varazdinska, Viroviticko-Podravska, Vukovarsko-Srijemska, Zadarska and Zagrebacka
as well as the capital Zagreb.
Head of State: President Ivo Josipovic, since February 19, 2010
Head of Government: Prime Minister Zoran Milanovic, since December 23, 2011
Language: the official language in Croatia is Croatian (Latin script). Serbo-Croatian (Cyrillic script) is spoken by the Serbian population. Minorities speak Italian, Hungarian, Czech, Slovak and German. (2001 census)
Religion: Roman Catholic 87.8%, Orthodox 4.4%, other Christians 0.4%, Muslim 1.3%, other or no information 0.9%, no religion 5.2% (2001 census)
Local time: CET. Between the last Sunday in March and the last Sunday in October there is summer time in Croatia (CET + 1 hour).
The time difference to Central Europe in both winter and summer 0 h.
International phone code: +385
Internet identifier:.hr
Mains voltage: 220 V, 50 Hz
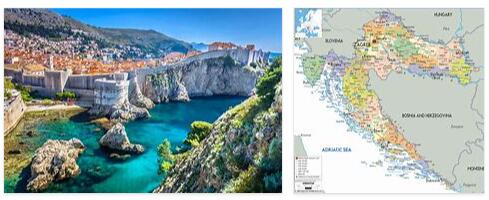
The Republic of Croatia is located in the northwest of the Balkan Peninsula and borders Slovenia in the north, Hungary, Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the east and Montenegro in the south. The Adriatic forms the natural border of Croatia in the west. The national territory covers about 56,500 square kilometers, including 1,185 islands, which are mostly on the Dalmatian coast, of which only 67 are inhabited.
Geographically, Croatia is divided into the fertile plains of Sava and Drava in the northeast, the mountainous Karstland in the north and in the center of the country, and the coastal region that is important for tourism. Viewed from above, you can see some mountain ranges rising out of the sea on the coast of the eastern Adriatic. Further east there are slowly descending clumps and chains that merge into an undulating hilly landscape. The hilly landscape of Slavonia spreads out between the wide river valleys of the Drava and Sava, from which a few higher mountain peaks protrude. On the left side of the Drava, a piece of the Hungarian Plain borders the north-west of Croatia. Visit watchtutorials.org for climate and weather in Croatia.
On the Makarska Riviera south of Split, the rugged rock massifs of the Biokovo Mountains extend all the way to the coast and offer an impressive panorama from these stretches of beach.
A steep limestone mountain range stretches from Rijeka to the Maslenica Bridge and from Split to the southeastern tip of Croatia. Also in the interior are rising mountain range that are repeatedly interrupted by deep river valleys. These zones, also called “Flysche”, are made up of limestone or sandy deposits rocks are very fertile and are used as arable land, meadows and pastures; in some regions wine is even grown.
The further you go from the coast to central Croatia, the more confusing an impressive mountain world rises – the Dinaric mountain region, which is also called Central Croatia or Croatian hill country. This region is mainly characterized by low mountain ranges and individual mountain ranges, which are characterized by hilly woodland, sudden depressions and many large poljes through which rivers run. The Dinaric mountain region includes the Gorski kotar mountain range, the Lika and Krbava high valleys and the Velebit mountain range, which runs along the coast.
A special natural phenomenon in this part of Europe is the karst. It arises on lime, which is dissolved by water, whereupon cavities form. The rainwater cannot run off and digs fine grooves in the rock, the so-called carts. From a certain depth, these in turn blast the limestone, so that the water gets through wider crevices into the underground, where it forms huge cave systems. There are caves everywhere, only a few of which have been explored or made accessible to visitors.
The wide and very fertile river valleys of the Drava and Sava are in stark contrast to the almost uninhabited and predominantly forested mountain ranges. On the completely flat river terraces During the Ice Age, a thick layer of loess built up, to which this region owes its agricultural character.
The Mediterranean coastal region, which is divided into three regions for historical reasons, is again completely different: the Istrian peninsula, which is joined by the Kvarner Bay, and Dalmatia in the south of the country. The Croatian coast has a total length of 1,780 kilometers.